Do you always feel a burning sensation in your chest, especially when you get up from sleep? Are you afraid to eat very spicy and hot foods during your work for fear of heartburn? This complaint has increased in the current century, and many questions remain about this heartburn. This heartburn appears as a result of prolonged untreated GERD , which is sometimes not positively affected by medications. Therefore, we will learn about esophageal reflux and discuss its most important causes and symptoms and how to treat and prevent it in the future.
Esophageal reflux
Esophageal reflux appears due to the weakness of the gastrostomy muscle, which leads to the reflux of acidic fluid from the stomach into the esophagus again. This causes irritation of the inner lining of the esophagus with a constant burning sensation during meals or other things. Some other diseases may also cause the possibility of reflux, such as the presence of hernias and the stomach taking long periods of time to digest and empty.
Symptoms of esophageal reflux
Symptoms gradually increase in severity over time without treatment and are as follows:
- Feeling a burning sensation in the chest, especially after meals, which increases in intensity at night
- Chest pain
- Difficulty swallowing
- Reflux of acidic food or drinks into the mouth again
- Feeling of a lump in the throat
If reflux is frequent at night, it may also cause:
- Chronic cough
- Inflammation of the vocal cords
- Sleep disorders
- chest allergy
Therefore, it is necessary to monitor the onset of such symptoms and seek medical advice as soon as possible.
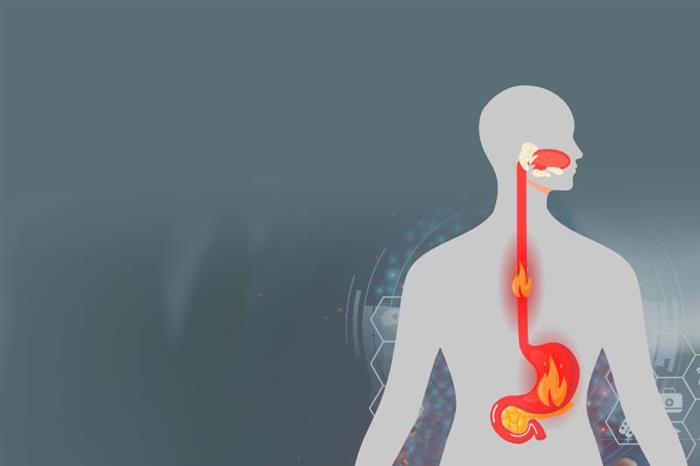
Risk factors
Some factors can increase the likelihood of developing esophageal reflux, such as:
- Obesity
- Abdominal protrusion or hernia
- Pregnancy
- Connective tissue diseases such as scleroderma
- Delaying gastric emptying
Other factors may cause increased stomach acid reflux, such as:
- Smoking
- Consuming large meals
- Eat late
- Eat fatty and fried foods
- Drinking alcoholic beverages that contain caffeine
- Taking some medications such as aspirin
When do you seek medical advice?
It is necessary to go to the hospital if you feel chest pain if it is accompanied by pain in the jaw or arm or an inability to breathe, because it may be an indication of the presence of angina pectoris.
But there are other cases that also require making an appointment with your doctor when you feel recurring symptoms of esophageal reflux or take medications to treat heartburn repeatedly during the week.
Doctor's questions
The doctor may ask a few questions before starting any tests to determine the primary causes of reflux, including:
- What symptoms are you feeling?
- When did you first feel it?
- Is it a frequent occurrence?
- Is there anything that relieves the severity of these symptoms for you?
- Do your symptoms wake you up at night?
- Do symptoms get worse after eating meals or when lying down?
- Do you feel sour food coming back up into your throat?
- Have you gained weight recently?
Diagnosis of esophageal reflux
It is easy to diagnose esophageal reflux through a clinical examination and the symptoms that the patient suffers from, but the doctor may request some tests to confirm reflux, find out which stages the patient has reached, and choose an appropriate treatment for him. There are many tests for esophageal reflux, including the following:
- Upper endoscope:
The doctor examines the esophagus and stomach by inserting a thin tube with a camera and light attached to it to clarify the vision. Esophageal biopsy may be done if any complications of reflux such as Barrett's disease appear.
- pH test:
A thin needle, like a catheter, is inserted through the nose into the esophagus and connected to a small computer to know when the stomach returns acid and for the exact duration of the reflux.
- Esophageal manometry:
This examination measures the number of muscle contractions in the esophagus when swallowing, and also measures the extent of the effort and cooperation of the esophageal muscles.
- X-ray of the upper gastrointestinal tract:
The x-ray shows a clear picture of the esophagus, stomach, and upper part of the intestine when the patient swallows a colored liquid that covers the inner lining of the digestive system. In addition, the doctor may ask to swallow a barium tablet to clarify the extent of the narrowing of the esophagus, which makes swallowing difficult.
Complications
Repeated esophageal reflux for long periods of time leads to difficult complications that affect the patient’s life in the future, such as:
- Esophageal stricture
The lower part of the esophagus is damaged due to repeated reflux of stomach acid, leading to the formation of scars that contribute to difficulty swallowing in the long term.
- Esophageal ulcer
Reflux causes the removal of esophageal tissue, which facilitates the appearance of ulcers and open wounds in the esophagus that bleed easily and cause pain and difficulty swallowing.
- Barrett's esophagus
The inner lining of the esophagus can be damaged as a result of increased reflux, which increases the risk of developing esophageal cancer later.
Treatment of esophageal reflux
Reflux can be treated with medications, surgery, and home prescriptions as well.
pharmaceutical
There are many medication options for reflux. It can be treated with medications that do not require a prescription, such as various antacids that reduce stomach acidity, but they alone do not treat stomach infections. There are also medications that reduce the production of stomach acid, but they do not work quickly to get rid of heartburn, but their effect lasts longer. The last option is medications that prevent acid production and treat the esophagus.
There are other medication options that require a prescription, such as medications that help strengthen the lower esophageal muscle, such as baclofen, H2 receptor blockers such as famotidine, and also proton pump inhibitors such as omeprazole and pantoprazole.
Surgical intervention
Medications usually treat and control the various symptoms of esophageal reflux, but in advanced cases in which medications are not effective and to prevent the appearance of complications, the doctor resorts to surgical intervention after looking at the health condition, age of the condition, and if other diseases are found that may disrupt the course of the operation.
Home recipes
Although some patients rely on natural recipes to find relief from heartburn, they have not been clearly proven effective in treating reflux symptoms. However, we find that some home suggestions can temporarily improve the severity of symptoms. For example, it has been found that some herbs, such as chamomile and licorice, help relieve heartburn pain, but a doctor must be consulted if there are other medical conditions that may conflict with them.
Some relaxation techniques and exercises can also help reduce the feeling of constant heartburn.
protection
Some people ignore prevention, even though it is sometimes more important than treatment and includes changing many habits, such as:
- Maintaining an ideal weight: Because being overweight puts pressure on the abdomen and increases acid reflux into the esophagus.
- Avoid smoking: because it affects the ability of the esophageal muscles to contract.
- Raising the head of the bed: A cement stone can be placed under the bed to raise the level of the head resting on the pillow, which in turn reduces acid reflux during sleep.
- Do not sleep immediately after meals: because this causes increased reflux.
- Eat slowly and chew quietly: this helps prevent indigestion.
- Avoid foods and drinks that stimulate acid reflux: Some foods, such as onions, garlic, spices, tomato sauce, mint, and also alcohol, can increase acid reflux.
- Stay away from tight clothes: because they put pressure on the abdomen and this contributes to acid reflux into the esophagus.