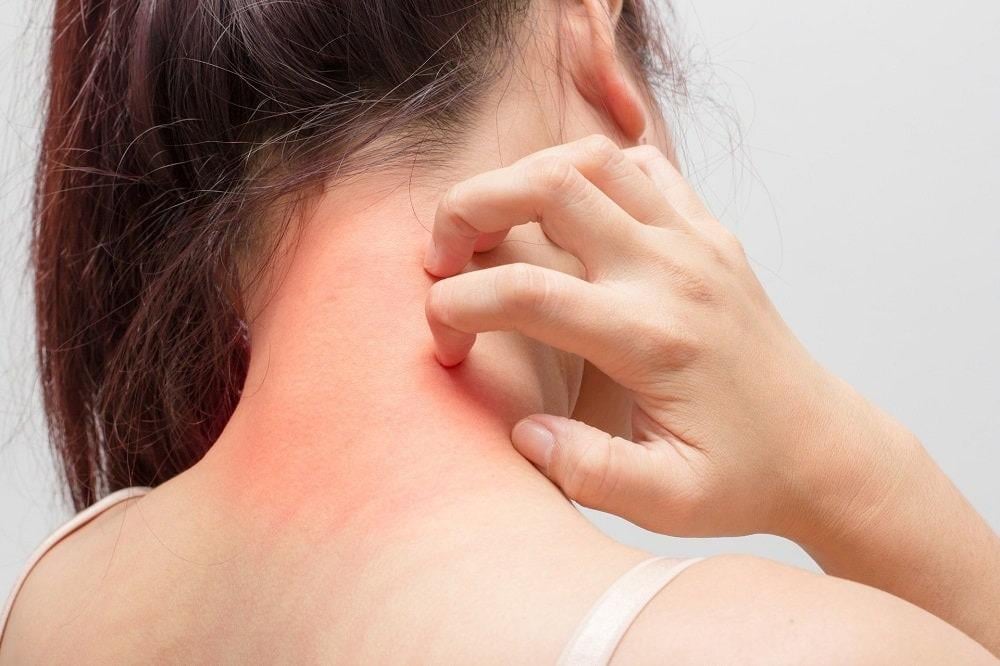
Facing winter always frightens some people, due to dry skin or atopic dermatitis (eczema) and the accompanying sleep disturbances and insomnia. Avoid heavy winter clothes for fear of constant itching, redness, and the appearance of dandruff if it comes into direct contact with the skin. Therefore, in this article, we will learn about eczema, discuss its causes, and find answers to questions about how to treat and prevent it during the different seasons of the year and the onset of winter.
What is eczema?
Eczema is one of the skin diseases that appear in the form of inflammation and redness of the skin with a constant desire to itch as a result of the attack of the internal immune system against some external causes. It often affects the extremities and areas that face some friction in the body. Children are most infected, but it can also infect adults.
Symptoms of eczema
The symptoms of eczema vary depending on the severity of the inflammation, sensitivity, and redness of the skin. It initially appears in the form of continuous itching, and its severity increases at night, which leads to redness and swelling of the area that was scratched. Then the crust appears as a result of itching in that area, and sometimes it even bleeds due to a scratch or wound. It may also appear as gray skin patches on the hands, feet, head, face, ankles, or chest.
Causes of eczema
The presence of allergy genes contributes to the appearance of eczema, such as vernal ophthalmia, chest allergies, or in people with allergic rhinitis or some food allergies in children. Continuous exposure to some chemical detergents, such as soap and cold water, among some people working in these fields, also affects the degree of hydration necessary to avoid eczema.
Diagnosis of eczema
There are no special laboratory tests to determine eczema, but the skin is examined and the person’s medical history is identified and it is also determined that there is a history of allergies in the family, because the itching of eczema is caused by the presence of a previous allergy in the patient or his family.
When do I seek medical advice and what are the doctor’s questions?
The patient's family can deal with the condition of the patient with eczema at home in its simplest form, but difficult cases require immediate medical consultation:
- Eczema can affect the patient's daily life, especially at night.
- An obvious skin infection causes yellow spots, pus, or severe dandruff to appear on the head or elsewhere.
- Symptoms continue to appear despite adherence to prevention and home treatment.
The doctor will manually examine the skin to identify the condition and ask you some questions
- When did these symptoms first appear?
- Do these symptoms occur frequently?
- Are these symptoms seasonal?
- What relieves symptoms?
- What makes your symptoms worse?
- Does anyone in your family suffer from eczema or chest allergies?
- What are your hobbies?
- Do you have a pet at home?
- What cosmetics do you use on your skin?
- What materials are your products made of?
- Do your symptoms affect sleep at night or affect your daily life?
Eczema treatment
The patient with inflammation takes two important directions: the first is the therapeutic pharmacological direction and the second is the non-pharmacological direction through prescriptions and home remedies.
pharmaceutical
- Ointments or creams containing cortisone are one of the topical methods that treat inflammation and must be applied immediately after moisturizing.
- Topical creams fight skin infections resulting from scratching and often contain antibacterial agents to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection, in addition to taking antibiotic tablets orally for a short period to get rid of the infection.
- Anti-inflammatory or cortisone tablets help calm swelling and redness in difficult cases, but they should not be taken repeatedly for long periods without consulting a doctor.
- Antihistamines or allergy medications help alleviate the severity of eczema at night, especially in children.
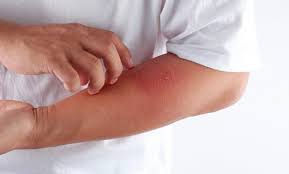
Eczema treatment
Home treatment
Non-drug treatment contributes to alleviating the severity of eczema and dry skin.
- Moisturize the skin twice daily with a suitable non-perfumed moisturizer.
- Avoid scratching the skin under any circumstances, even if it is necessary to cut the nails to reduce the child’s itching.
- Use bandages and plasters on the affected skin to avoid constant itching, which in turn reduces the appearance of dandruff.
- Avoid using water for long periods because it causes obvious side effects and increases the possibility of dehydration
- Dive or bathe in a warm bath for no more than 15 minutes, then gently dry the skin and apply moisturizer to the body while it is still completely wet.
- Use lotions and soaps that are free of detergents and harmful chemicals on the skin.
- Use an air purifier to avoid dry air in the room for long periods, as this helps increase itching and dry skin.
- Wear soft cotton clothes and avoid clothes that consist of threads or coarse wool directly on the skin.
- Avoid stress and poor psychological state in the affected person because it increases the severity of eczema. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention and take good care of mental health also in stressful moments to avoid skin inflammation and itching associated with stress.
Risks
Persistent skin infections affect the body and pose long-term risks.
- Eczema leads to chest allergies, asthma, and hay fever.
- Skin infections affect its nerve endings due to constant itching, and then the skin crust turns into chronic crust.
- Eczema increases the possibility of various skin infections, because itching opens wounds and exposes them to various bacteria and viruses.
- Constant exposure to detergents and cold water can cause persistent inflammation and redness.
- A person suffering from eczema suffers from several sleep disorders.
protection
Because prevention is better than a thousand cures, eczema requires its own prevention that is easy to follow, especially with a young child’s age
- Constantly moisturize the skin using suitable non-perfumed moisturizers that do not contain a high percentage of alcohol.
- Bathing and exposure to water for short periods reduces dehydration.
- Knowing the allergens in food, dust, or pollen reduces exposure to them and reduces the severity of skin irritation.
- Avoid using antiseptic or perfumed soaps because they remove skin oils and increase dryness.
- Dry the skin after showering using a soft cotton towel and avoiding rough towels. This helps keep the body moisturized.
- Drink fluids and water constantly to avoid dehydration.
- Also, eating vegetables and fruits is a suitable treatment for eczema because they contain high amounts of fluids, such as cucumbers, watermelon, lettuce, oranges, and other fibers that contribute to skin moisture.
- Limit caffeine, such as tea, coffee, and soft drinks, as they draw water from the body and increase the possibility of dry skin.
Therefore, constantly moisturizing the skin helps reduce skin infections and avoid skin diseases and eczema in the future.